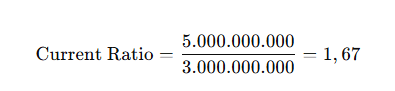Understanding Current Ratio: Formula, Meaning, and Examples in Financial Analysis
2025-10-08
Bittime - In financial analysis, the liquidity ratio is an important benchmark to evaluate a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations. One of the most commonly used liquidity ratios is the Current Ratio.
This ratio compares total current assets to total current liabilities to determine an entity’s ability to pay short-term debts.
In this article, we will discuss the definition, formula, examples, interpretation, advantages & limitations of the current ratio in depth.
What Is Current Ratio?
The current ratio is a financial ratio that measures a company’s ability to cover short-term liabilities (current liabilities) using short-term assets (current assets).
This ratio indicates how secure a company is under normal liquidity conditions.
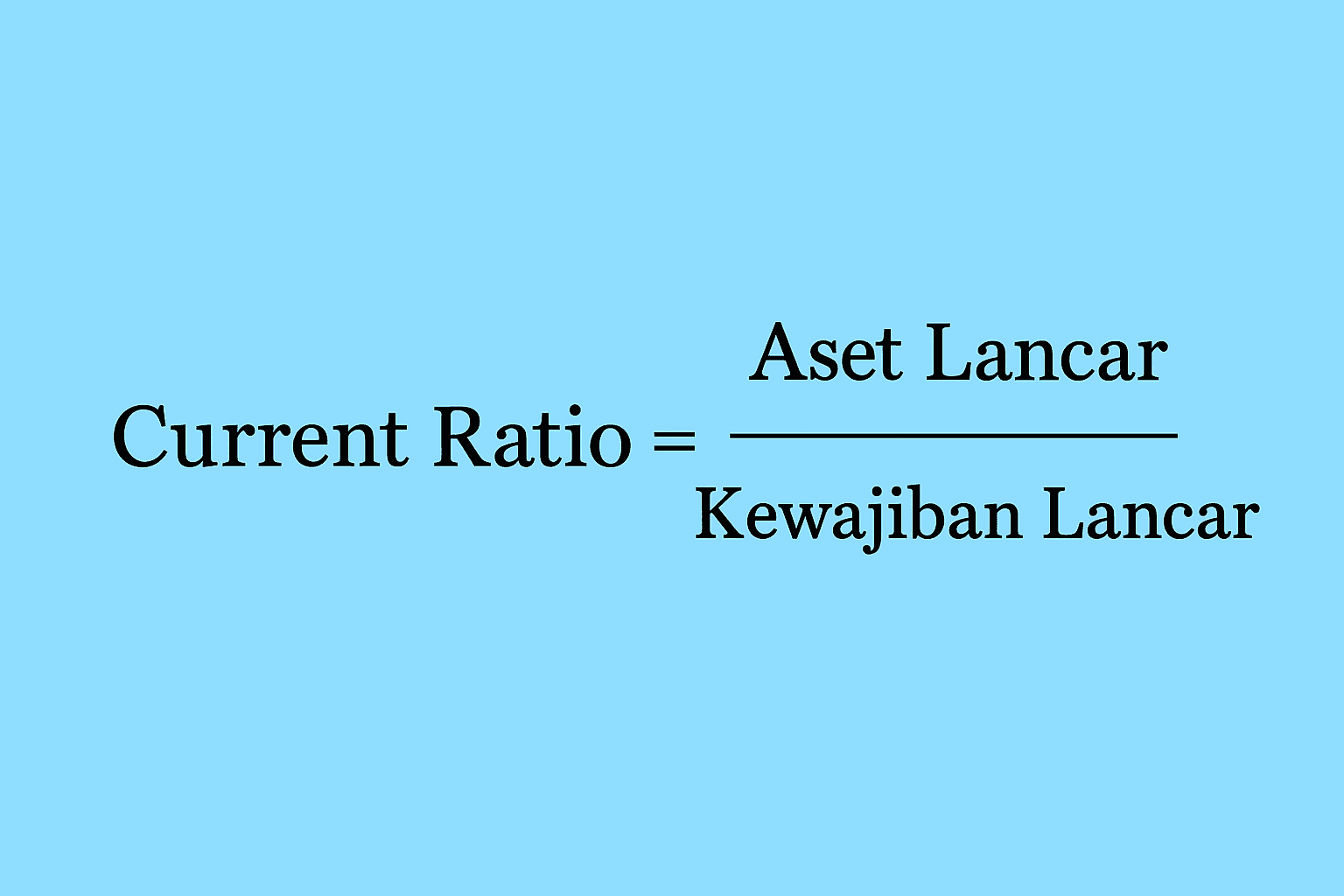
Simply put, current ratio = (current assets) ÷ (current liabilities).
If the result is greater than 1, it means the company has more current assets than short-term liabilities—indicating a relatively safer liquidity position.
Read Also: Understanding Crypto Lending: Interest, Collateral & How to Borrow Correctly
Formula and Components of Current Ratio
Basic formula of the current ratio:
Current Assets include:
- Cash and cash equivalents
- Accounts receivable
- Inventory
- Other current assets (prepaid expenses, etc.)
Current Liabilities include:
- Accounts payable
- Accrued expenses
- Short-term debt (loans due < 1 year)
- Current portion of long-term debt
Example Calculation of Current Ratio
For example, a company has:
- Current assets = IDR 5,000,000,000
- Current liabilities = IDR 3,000,000,000
So:
This means the company has IDR 1.67 in current assets for every IDR 1 of current liabilities, indicating relatively good liquidity.
Read Also: Bilateral Trade: Definition, Advantages, and Disadvantages
Interpretation of Current Ratio
- < 1.00: The company may have difficulty meeting short-term obligations.
- = 1.00: Current assets are sufficient to cover current liabilities.
- > 1.00: The company has extra “liquidity buffer.”
- Too high (e.g., > 3.00): May indicate inefficient use of assets (idle capital).
However, the best interpretation is to compare the current ratio with the industry average and observe trends over time.
Advantages and Limitations of Current Ratio
Advantages
- Easy to calculate and understand
- Provides a quick picture of short-term liquidity
- Useful for comparing across periods or between companies in the same industry
Limitations
- Does not consider asset quality — e.g., receivables that are hard to collect or inventory that is hard to sell
- Does not show instant liquidity (some assets may not be quickly converted to cash)
- Can be misleading if a company has a very high ratio but low efficiency
- Not suitable for comparisons across very different industries
Read Also: Multilateral Trade: Definition, Advantages, Disadvantages, and Examples
How to Use Current Ratio in Financial Analysis
- Use it together with other liquidity ratios such as the quick ratio or cash ratio.
- Observe ratio trends year over year — is liquidity improving or deteriorating?
- Compare with the industry average or main competitors.
- Examine the components of assets and liabilities to understand whether current assets are truly easily liquidated.
Read Also: What Is Winrate: Definition and Formula for Calculation
Conclusion
The Current Ratio is an important indicator for assessing a company’s short-term liquidity health.
Although not perfect, when used together with other analysis tools and within an industry context, this ratio helps investors and analysts understand financial risk and short-term solvency position.
How to Buy Crypto on Bittime
Want to trade or buy Bitcoin and invest in crypto easily? Bittime is ready to help! As an Indonesian crypto exchange officially registered with Bappebti, Bittime ensures every transaction is safe and fast.
Start by registering and verifying your identity, then make a minimum deposit of IDR 10,000. After that, you can immediately buy your favorite digital assets!
Check rates BTC to IDR, ETH to IDR, SOL to IDR and other crypto assets to see the crypto market trend today in real time on Bittime.
Also visit Bittime Blog for interesting updates and educational information about crypto. Find trusted articles on Web3, blockchain technology, and digital asset investment tips designed to enrich your crypto knowledge.
FAQ
What is current ratio?
The current ratio is a financial ratio that compares current assets to current liabilities to evaluate a company’s ability to meet short-term obligations.
How to calculate current ratio?
By dividing total current assets by total current liabilities: Current Ratio = Current Assets ÷ Current Liabilities.
What is a good current ratio value?
Generally, between 1.5 and 2.0 is considered healthy, but the optimum depends on the industry. A ratio > 1 already indicates that current assets exceed current liabilities.
What are the weaknesses of current ratio?
It does not account for asset quality (e.g., uncollectible receivables), and can be misleading if the value is too high, indicating many idle assets.
Is current ratio the same as quick ratio?
No. Quick ratio excludes inventory and less liquid assets, providing a more conservative view of immediate liquidity.
Disclaimer: The views expressed belong exclusively to the author and do not reflect the views of this platform. This platform and its affiliates disclaim any responsibility for the accuracy or suitability of the information provided. It is for informational purposes only and not intended as financial or investment advice.