Bitcoin Whitepaper in Indonesian: Complete Guide and Discussion
2025-10-08
Bitcoin Whitepaper in Indonesian: Complete Guide and Discussion
The Bitcoin whitepaper is a foundational document that outlines Satoshi Nakamoto's vision for a decentralized electronic cash system. Published on October 31, 2008, this whitepaper introduces a peer-to-peer network that allows value to be sent without intermediaries, solving the double-spending problem and high fees in digital payments.
We will discuss the contents of the Bitcoin whitepaper in Indonesian in an enjoyable and easy-to-understand way.
The Bitcoin whitepaper consists of several important sections, from the introduction to transaction mechanisms. This document explains how the network addresses the limitations of traditional financial systems that rely on third parties to process payments.
Through simple technical explanations, readers can understand basic concepts such as digital signatures, proof-of-work, and how blockchain works.
Also Read: 7 Effective Crypto Trading Tips for Beginners, Complete with Tips and Tricks
Structure of the Bitcoin Whitepaper (BTC)
The Bitcoin whitepaper consists of several main sections. Each section helps explain how this digital money system works. Here is a summary of the document's structure:
Introduction
- Trust issues in traditional financial systems: The whitepaper explains that online trading heavily depends on financial institutions acting as intermediaries. This dependence incurs mediation costs and limits small transactions.
- Solution through cryptography: Satoshi emphasizes the need for an electronic payment system based on cryptographic proof that allows two parties to transact directly without intermediaries. This system must be resistant to double-spending and protect sellers from fraud.
- Introduction to blockchain: The concept of a distributed ledger is introduced, showing how a peer-to-peer network can replace a central authority with network consensus.
In the introduction, readers are introduced to why Bitcoin is necessary. Satoshi describes how the costs and uncertainty of payments in traditional systems can be avoided with this new technology. He highlights the importance of privacy and greater control for users.
Bitcoin Transactions (BTC)

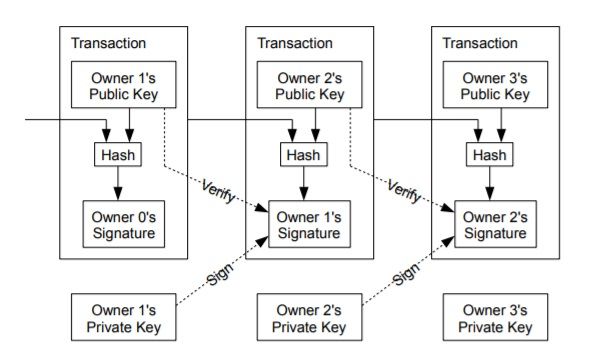
- Definition of an electronic coin: The whitepaper defines a coin as a chain of digital signatures where the previous owner signs the hash of the previous transaction along with the public key of the receiver. This ensures a verifiable ownership chain.
Double-spending issue: While digital signatures can validate ownership, the receiver cannot be sure that the coin has never been double-spent.
Traditional solutions involve a central authority to verify each transaction, but this creates dependence on third parties.
Peer-to-peer solution: Satoshi proposes that transactions be broadcast publicly through the network. Network participants must agree on the order of transactions to prevent double-spending.
In this way, the first transaction broadcasted is considered valid, while fraudulent attempts are not recognized.
This section explains how blockchain replaces the role of a central authority in overseeing transactions. Instead of relying on banks, a global network of nodes acts as a collective supervisor, ensuring that no coin can be used more than once.
Bitcoin Network and Proof-of-Work (BTC)
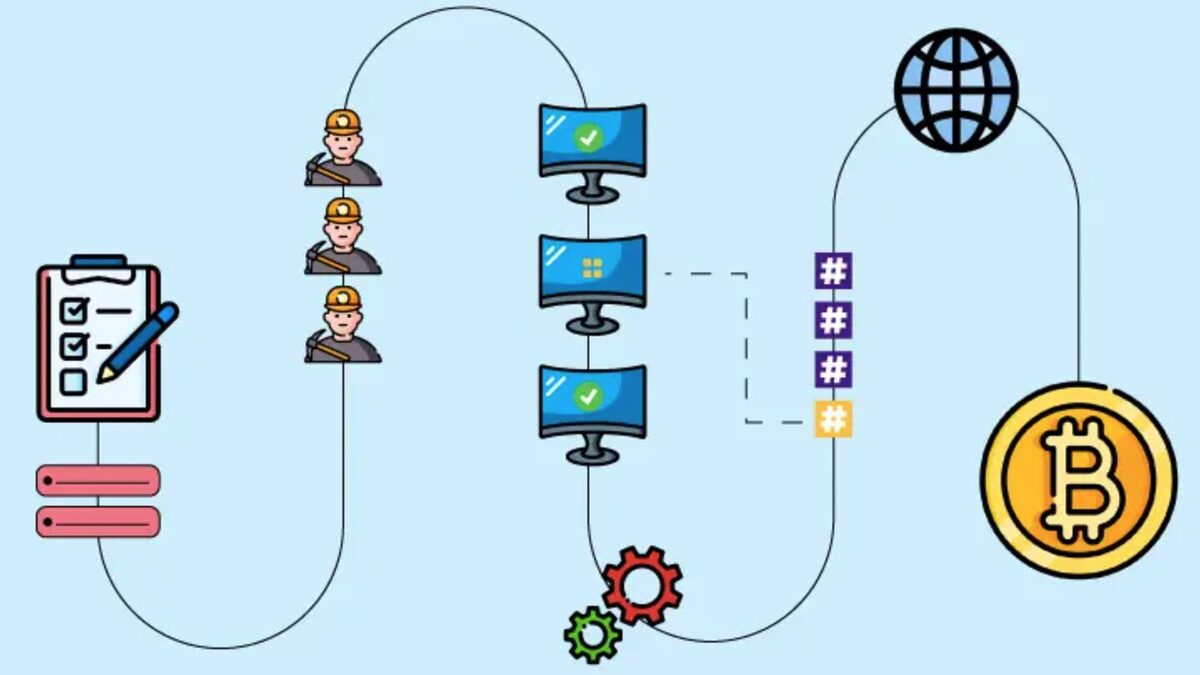
Network steps: The whitepaper details Bitcoin's network process in six steps — starting from the broadcasting of new transactions, grouping transactions into blocks, searching for proof-of-work, to block acceptance by other nodes.
Nodes always consider the longest chain as the valid chain and continue to extend it.
Proof-of-work: Finding a hash that meets a certain difficulty requires computational effort. This proof becomes the mechanism to secure the network and prevent block duplication attacks.
The longer the chain, the greater the proof-of-work already completed, and the harder it is to alter.
Tolerance to disruptions: The network is designed so that messages are broadcast on a "best effort" basis. Nodes may join or leave the network at any time without damaging the integrity of the blockchain.
If two new blocks are broadcast at the same time, nodes will choose the block that was received first and store the other branch in case that branch becomes longer.
This section explains how consensus is achieved through the proof-of-work competition. This process ensures that no single entity can control the network, thus transactions remain secure and well-verified.
Also Read: How to Play Crypto for Beginners, Most Updated 2024
Bitcoin Incentives and Security (BTC)

- Creation of new coins: The first block in the blockchain contains a special transaction that creates new coins as a reward for the node that successfully finds proof-of-work. This incentivizes miners to support the network.
- Transaction fees: As the coin supply increases, the incentive slowly comes from transaction fees. The difference between the input and output of a transaction becomes an additional fee added to the block reward.
- Honesty and security: The incentives make miners more likely to follow the rules rather than attack the network. If an attacker has significant computational power, they are better off mining new coins than invalidating transactions and compromising the network's integrity.
- Block summary and Merkle Tree: The whitepaper explains the Merkle Tree technique to summarize transactions within blocks and save storage space.
The incentives section shows that Bitcoin is not just a technology but also an internal economy. By rewarding miners, the network's security is maintained and remains decentralized.
Miners play the role of ledger keepers, ensuring that transactions are processed honestly.
Conclusion
The Bitcoin whitepaper introduces a digital payment system that operates without relying on intermediaries. The document shows how a peer-to-peer network with proof-of-work can prevent double-spending and maintain ledger integrity.
The success of the network depends on the majority of honest nodes holding the majority of computational power. Its design is simple but powerful: nodes are free to join and leave, messages are broadcast on a best-effort basis, and all rules are enforced through consensus.
Visit Bittime Exchange to create an account and make your first purchase. Don’t forget to read other educational articles on Bittime Blog to enrich your crypto knowledge.
FAQ
What is the Bitcoin whitepaper?
The Bitcoin whitepaper is a document that explains the concepts and technical details of Bitcoin. This document outlines a decentralized digital money system that allows peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries.
Why is understanding the Bitcoin whitepaper important?
Understanding the whitepaper helps you grasp the basic principles of blockchain and how Bitcoin solves trust issues in traditional payment systems. It provides insight before you start investing.
How does proof-of-work work in Bitcoin?
Proof-of-work is a mechanism where miners use computational power to solve cryptographic puzzles. The result is proof that effort has been made, and a block containing new transactions can be added to the blockchain.
Is there a Bitcoin whitepaper in Indonesian?
Yes, there is an official translation of the Bitcoin whitepaper in Indonesian. This translation helps local readers understand the content of the document without language barriers.
Where can I find information about Bitcoin trading?
You can access Bittime Exchange to start trading Bitcoin and other crypto assets. For the latest news and guides, visit the Bittime Blog.
Disclaimer: The views expressed belong exclusively to the author and do not reflect the views of this platform. This platform and its affiliates disclaim any responsibility for the accuracy or suitability of the information provided. It is for informational purposes only and not intended as financial or investment advice.